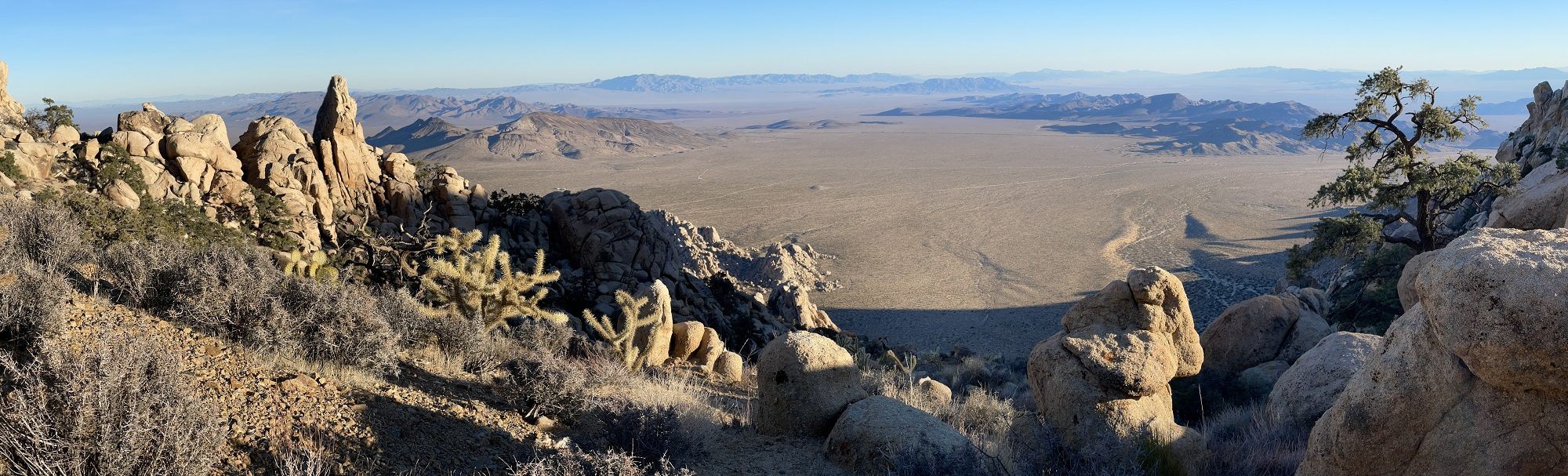
In my twenties, I basically lived in the desert — just outside of the Mojave at 6,000′ in the San Gabriel Mountains. I was minutes from Joshua trees (Yucca brevifolia) that define a particular charm in the Mojave Desert . I spent many winter weekends wandering the Sonoran and Mojave deserts of California and Arizona. It was dreamy.
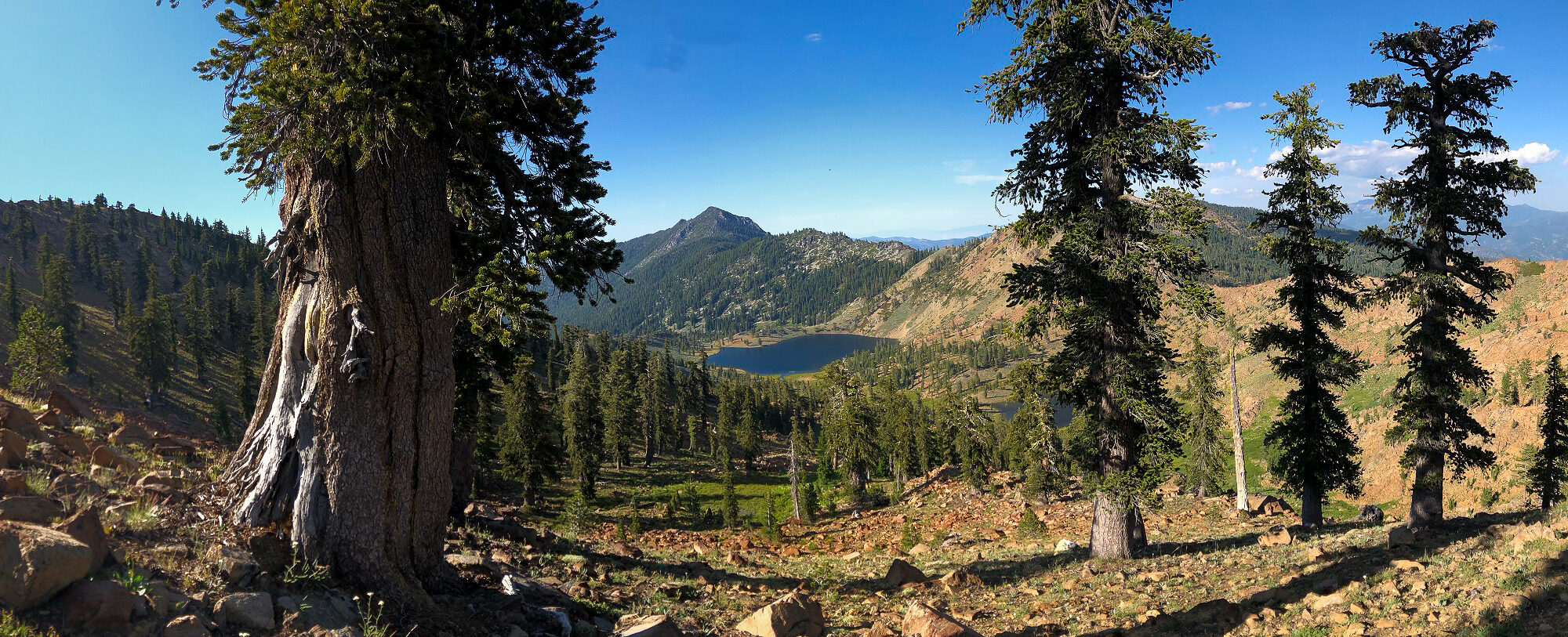
After moving north to the temperate rainforest of Humboldt County to pursue a more stable career and more conifers, the desert has become a less common destination. I have been back a few times but, honestly, not enough.
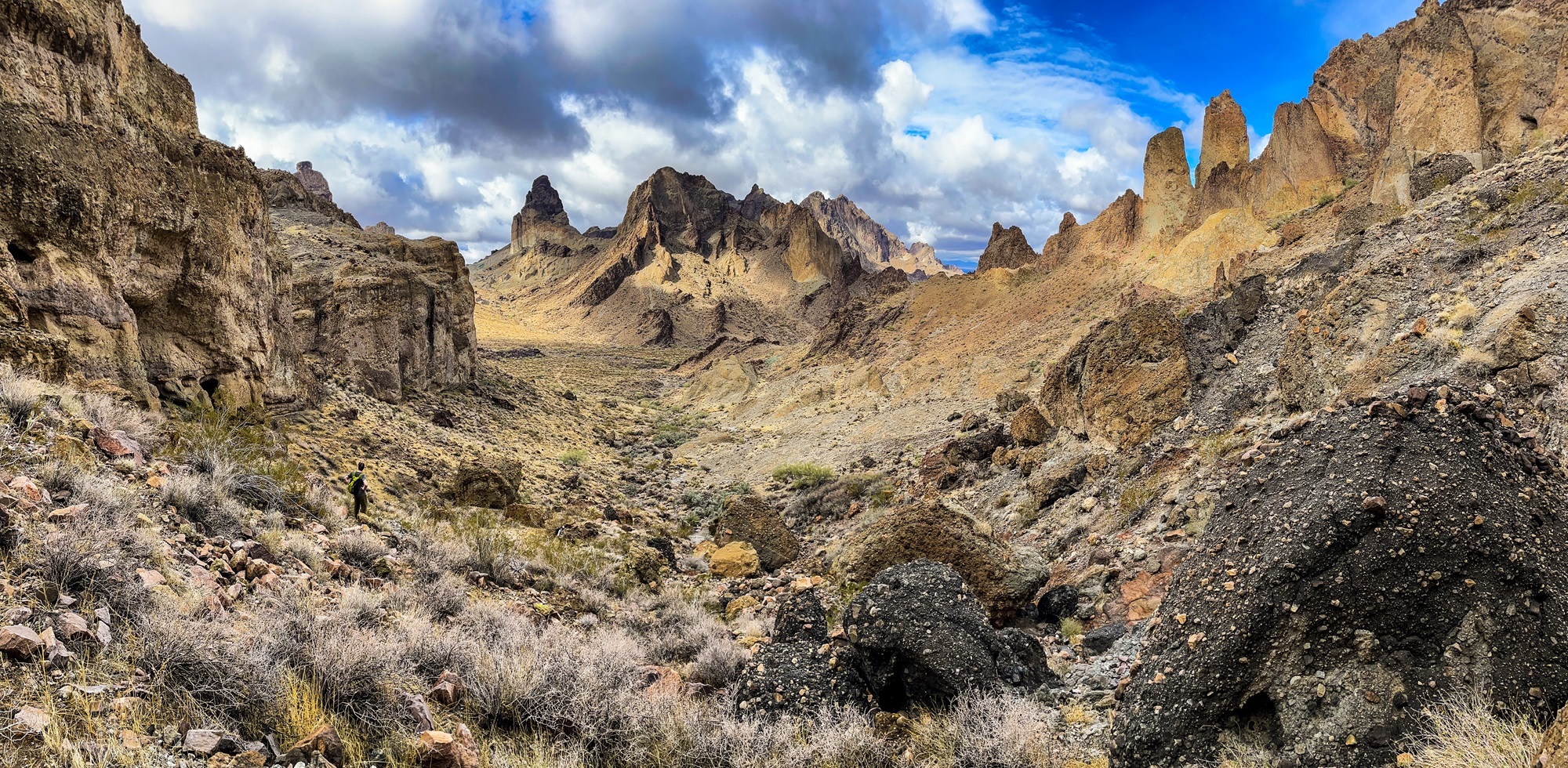
With 50 on the horizon, a few of my friends decided to meet up in Las Vegas and get into the desert as fast as possible. We spent time in the Mojave-Sonoran transition zone south of I-40 and could not have been happier–walking washes and scrambling through canyons. We saw new plants, plenty of rain, and reflected on our first half century around numerous campfires.
Continue reading “Approaching 50 in the Desert”